Taxes are complicated.
They’re not hard, they’re complicated.
Federal income tax is complicated in the same way that old computer systems are complicated. As a software developer, it’s not uncommon for you to update old code to perform new functions. What often happens, especially in poorly designed systems, is that you just update the code. You don’t redesign the system, known as refactoring, with the new functionality — you just add it to the existing system.
As you’d expect, over many years, systems built this way don’t operate as efficiently.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, signed in 2017, amended the Internal Revenue Code of 1986. That was over three decades later!
But that’s neither here nor there because today I want to talk about estimated taxes. And estimated taxes are often made out to be this complex system where you have to do things a perfect way or you’ll get in trouble.
It’s not complicated and I’ll explain exactly how they work.
Table of Contents
🔃Updated January 2024 with figures and dates for 2024 and updated screenshots for the worksheets included in 2024 Form 1040-ES: Estimated Tax for Individuals.
What Are Estimated Tax Payments?
Our tax code requires you to pay taxes as you earn income.
If you’re a W-2 employee, you have tax withheld on every paycheck by your employer. This is based on what you enter on a Form W-4.
At the end of the year, you fill out your tax return, figure out your actual tax liability, and pay the difference or get a tax refund. Easy right?
Well, if you earn any income outside of a job that withholds your taxes, such as if you’re a self-employed individual, then you’ll need to pay estimated taxes. You may also need to make estimated tax payments if you’ve received any other non-work income that isn’t subject to income tax withholding, such as capital gains.
You should be making these estimated tax payments each quarter based on your expected adjusted gross income. The idea is that these quarterly estimated payments will be close enough to withholding.
There is one exception though, known as the safe harbor rule.
What Are the Safe Harbor Tax Rules?
The IRS knows that people who aren’t working a traditional W-2 job might have irregular income. So they offer some leeway and won’t punish you if you’re a little short.
The safe harbor provisions are:
- If you expect to owe less than $1,000 after subtracting your income tax withheld, you’re safe.
- If you pay 100% of the previous year’s tax liability via estimated quarterly tax payments, you’re safe. If your adjusted gross income for the year is over $150,000, then it’s 110%.
- If you pay 90% of your current year’s tax liability, you’re safe.
So they expect you to be close (or over), and won’t penalize you if you don’t get it exactly right.
There are also special rules for farmers, fishers, and certain high-income taxpayers. Your state will also have estimated tax payment rules that may differ from the federal rules.
Making Estimated Tax Payments: Due Dates for 2024
The estimated tax payments are due quarterly. And those dates are roughly the same each year: the 15th of April, June, September, and the following January.
From time to time the actual day slides, due to holidays and weekends.
For the 2024 tax year, the dates to pay estimated taxes are:
| Earning Period (Quarter) | Due Date |
|---|---|
| First Quarter (income earned Jan – March) | April 15th, 2024 |
| Second Quarter (income earned April – June) | June 17th, 2024 |
| Third Quarter (income earned July -Sept) | September 16th, 2024 |
| Fourth Quarter (income earned Oct – Dec) | January 15th, 2025* |
Calculating Estimated Tax Payments
If you have self-employment income, there are two parts to calculating how much you need to pay. The first involves self-employment tax. Self-employment taxes add a wrinkle when calculating what you owe but the IRS can help.
The IRS has a worksheet included in the Form 1040-ES package that you can use to calculate it better based on your expected income:
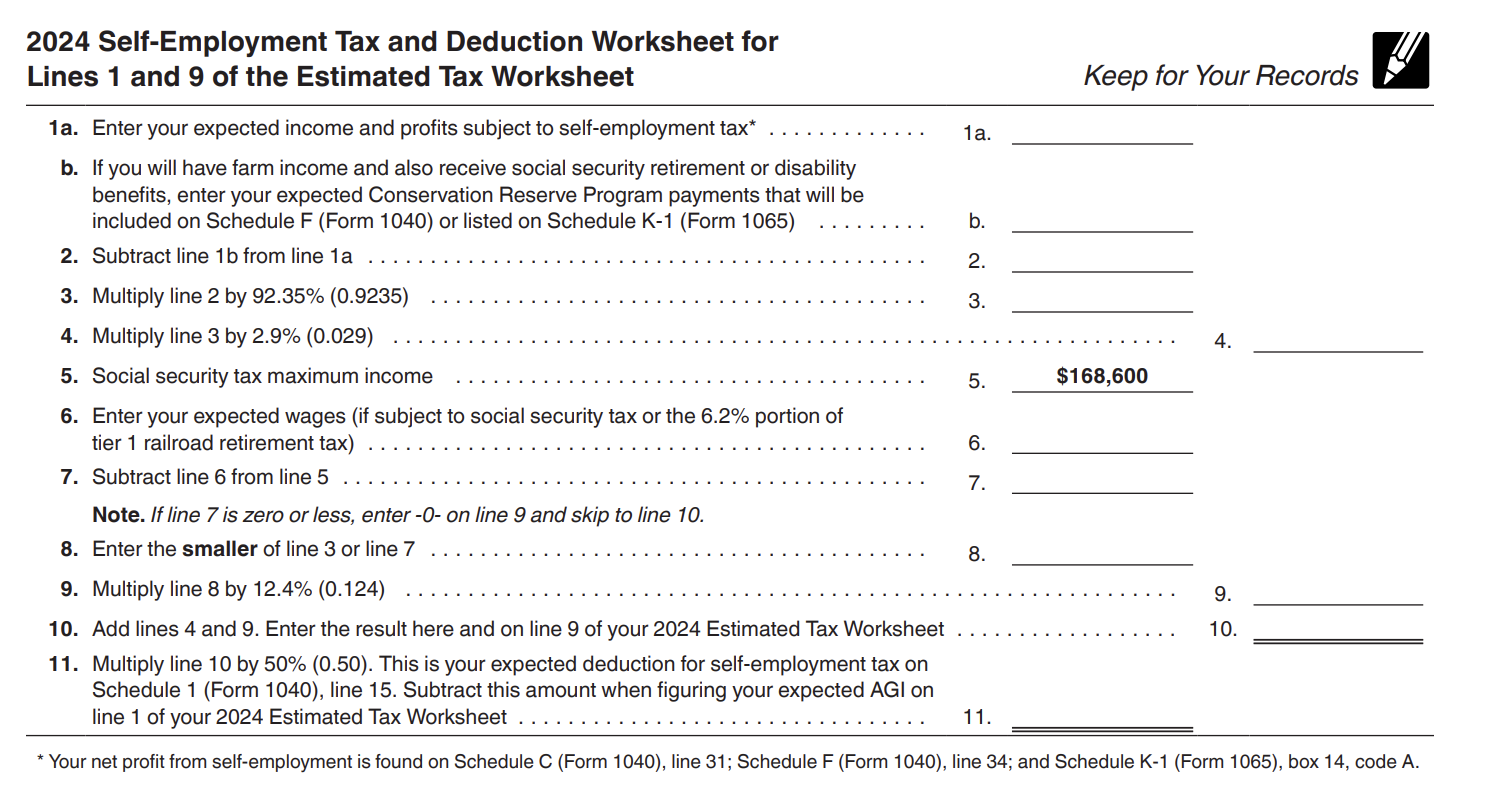
That same workbook has a tax rate schedule you can use to calculate the taxes you might owe. Use that to figure your estimated payments and you’ll likely be within the 90% safe harbor rule.
Next, you’ll need to check out page 8 of the document for the estimated tax worksheet, which relies on your income and tax bracket to figure out your taxes due:

How to Pay Estimated Taxes to the IRS
If you want to make your payment online, there are several options on the IRS website for paying your taxes. One of the most common is to use the Electronic Federal Tax Payments System to make your estimated payments, but that requires creating another account you will need to manage.
Personally, I just pay via mail because then I have a canceled check as my record. It’s how I’ve done it for years so I never felt a need to change it. You can start by downloading Form 1040-ES and the payment vouchers are on pages 10 and 11.
Where you send your payment depends on where you live, just like where you would mail your tax returns (yo, e-file! you get your tax refund faster!).
| Where You Live | Where To Send |
|---|---|
| Alabama, Arizona, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, New Mexico, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas | Internal Revenue Service P.O. Box 1300 Charlotte, NC 28201-1300 |
| Arkansas, Connecticut, Delaware, District of Columbia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Missouri, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, Vermont, Virginia, West Virginia, Wisconsin | Internal Revenue Service P.O. Box 931100 Louisville, KY 40293-1100 |
| Alaska, California, Colorado, Hawaii, Idaho, Kansas, Michigan, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, Ohio, Oregon, North Dakota, Pennsylvania, South Dakota, Utah, Washington, Wyoming | Internal Revenue Service P.O. Box 802502 Cincinnati, OH 45280-2502 |
| A foreign country, American Samoa, or Puerto Rico | Internal Revenue Service P.O. Box 1303 Charlotte, NC 28201-1303 |
| Guam | Department of Revenue and Taxation Government of Guam P.O. Box 23607 GMF, GU 96921 |
| U.S. Virgin Islands | Virgin Islands Bureau of Internal Revenue 6115 Estate Smith Bay, Suite 225 St. Thomas, VI 00802 |
If you need to speak to someone at the IRS, here is how to reach a live person at the IRS.
Can I Make Unequal Payments?
Generally, you should make estimated tax payments in equal amounts, but it’s OK if some are larger than others due to irregular income.
Most people calculate the safe harbor amount, add some wiggle room, divide by four, and pay that amount. It’s easier to calculate that way and it’s just as safe from a tax perspective — just make sure to keep enough aside in case you have a good year and owe more in federal taxes come April.
Also, for the last payment in January, you don’t need to make it if you file your tax return by January 31st.
What If I Fail to Pay?
If you don’t pay enough, the IRS will assess an underpayment penalty. You’ll just owe taxes plus a bit for the penalty.
However, if your failure to pay is due to a disaster or other unusual circumstance or if you retired or became disabled during the tax year of the estimated payments, the underpayment penalty may be waived.
The Bottom Line
If you don’t have taxes taken off your paycheck, your estimated taxes need to be paid quarterly, to avoid penalties come tax time. But, since it’s difficult to guess your total tax liability (especially if you have self-employment or irregular income), the safe harbor rule acts like a safety net.
So long as you pay the previous year’s estimated tax liability or close to the current year’s liabilities, you’ll safely avoid unnecessary penalties.




This is the most straightforward write-up I’ve ever read on estimated taxes, Jim. Thank you for this – it’s something I need to be on top of now that I’m starting to see some decent income from my side hustles.
— Jim
Thanks Jim! And it’s great you need to pay estimated taxes! 🙂
Where in my 2018 Form1040 do I find the amount of taxes paid for the Safe Harbor calculation? Is it line 15?
I believe it is line 61 or 63.
I’m helping to sell a parent’s house, to use the proceeds toward assisted living.
The parent earned only Social Security and did not file a return last year.
The house was sold for a sizable capital gain. At what point is the tax on that gain due? Is there a way to take advantage of safe harbor rules to avoid paying the tax until April 15th to maximize interest income on the proceeds?
They are allowed to exclude $250,000 of gain (each) on the sale of the home. So if you have two parents, that’s $500,000 of gain. If you have one, that’s $250,000 of gain.
I’m afraid I don’t know the rules for safe harbor based on a previous year’s taxes when you didn’t file in the previous year. If the IRS treats it as having paid $0, then you would be safe regardless since 100% of $0 is still $0. I’d call a tax accountant to find out, I suspect it’s a simple question and they wouldn’t charge you for it.
I have two rentals. Generally speaking, are the Safe Harbor Rules worth looking into (assuming I meet the requirements). Im retired with no other side jobs. Thank you
I’m afraid I can’t offer specific tax advice for your situation but you always want to make sure you’re paying what you need to or you run the risk of penalties.
My husband died on March 31, 2019. My daughters moved me into an assisted living place on April 30. In the moving process, I was in “la, la, land” and not able to make many decisions. On our income tax, we took a safe harbor deduction on his pension from teaching in a California High School as they did not pay into social security. My husband had a formula for that deduction that he said never changes. My daughter took all of my records as I asked her husband to help me with my taxes this year. I had the… Read more »
I’m afraid that equation is likely associated with the pension itself and not a universal equation for all pensions? I’m afraid I don’t know and you’ll have to look in the records for the specific figure. I’m sorry I couldn’t be of more help.
I am converting part of my IRA to a ROTH. I know I will owe taxes on about 98% of the amount I am converting because I have some non-deductible amount in that IRA. My question is do I have to pay estimated taxes quarterly or can I pay the amount to keep me within the Safe Harbor Rule annually or in Sept and January without incurring a penalty? I know the first quarterly (April ) is being moved to July, so do I have to pay in thirds for the year?
I would speak to a tax accountant to get an accurate answer based on your scenario – thanks!
If I am w2 does the safe harbor rule still apply? So if I simply pay 100% or 110% of previous years tax bill will there be zero penalty?
It applies to all taxpayers, just pay as much as the safe harbor rules require and you’re OK.
I had some capital gains in stock sales and I plan to use the safe harbor rule of paying 100% or 110% of my previous tax year liability for Federal tax. My cap gains came throughout the year un-uniformly. I am a salaried employee and have payroll tax deductions. I adjusted my payroll deductions to make sure I paid 100% or 110% of previous tax year liability for safe harbor, but not planning to do any estimated qtrly payments. Any issues with this? I assume the IRS doesn’t care if the money comes from payroll deductions or estimated payments. As… Read more »
I’m not a tax accountant so take this with a grain of salt – as far as I know, there is no difference between making quarterly estimated payments or having your deductions be a little larger. Making the estimated payments is just a little bit easier than going to your company’s HR to ask them to withhold more. It’s still money going to the IRS. 🙂
I’m a salaried employee with a W-2, but have a large taxable capital gain in 2020 Q4. Due to 401k catch-up, my salary witholdings are not going to be 110% of my 2019 taxes to avoid estimated taxes. My plan was to pay Q4 estimated taxes to get the total withheld & paid above 110% of 2019, even though I know I will owe more based on the large gain. This should avoid a penalty under the safe harbor, correct?
JB – I recommend talking to a tax accountant to get a full answer for your specific situation.
If I were in this situation, I would make a Q4 estimated payment and chances are it’ll be OK. Honestly, there isn’t really another option anyway!
I’ve used the safe harbor rule for ỳears but it won’t work for 2021 since required minimum distributions were not included which also affects th amount of Social Security taxes paid. So what do we use, 2019 taxes? Or just try to figure the estimated taxes using the worksheet (bummer)
Perhaps I’m not understanding your question but my understanding is that you could still use your 2020 figures?